Supply chain execution refers to the process of managing and optimizing the operational aspects of a supply chain to ensure that products are delivered efficiently and effectively from suppliers to customers. It encompasses various activities, with supply chain execution software, including a best-in-class WMS, often integrating these functions to ensure seamless operation. Effective supply chain execution follows supply chain management trends and supply chain management strategies to enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction by ensuring accurate and timely product delivery.
In this article, we’ll cover:
- Key supply chain execution activities
- What are the 5 stages of the supply chain process?
- What are the benefits of supply chain execution?
- Different types of supply chain execution systems
- Made4net’s supply chain execution software?
Key supply chain execution activities
- Order Fulfillment: Managing and processing customer orders, ensuring timely delivery, and meeting customer expectations.
- Inventory Management: Tracking and controlling inventory levels to balance supply and demand, minimize holding costs, and avoid stockouts or overstock situations.
- Warehouse Management: Overseeing the storage, handling, and movement of goods within warehouses to maximize efficiency and accuracy.
- Transportation Management: Planning and coordinating the movement of goods from suppliers to customers, including selecting carriers, optimizing routes, and managing freight costs.
- Supplier Coordination: Collaborating with suppliers to ensure timely delivery of raw materials and components, and maintaining quality standards.
- Logistics Execution: Managing the end-to-end logistics process, including the orchestration and integration of transportation, warehousing, and inventory management.
What are the 5 stages of the supply chain process?
Supply chain execution is just one of the stages within the overall supply chain management process. These five stages work together to ensure that products are efficiently produced, delivered, and managed throughout the supply chain.
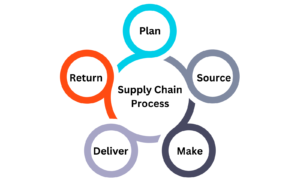
What is supply chain planning?
Supply chain planning focuses on developing a strategy for managing resources, production, and distribution. It includes forecasting demand, setting inventory levels, and aligning supply chain activities with business objectives. This stage ensures that all resources are effectively allocated to meet future needs. Proper planning helps minimize disruptions and optimize operational efficiency. It lays the groundwork for a well-coordinated supply chain.
What is supply chain sourcing?
Supply chain sourcing focuses on selecting and managing suppliers who provide essential raw materials or components. This stage includes procuring the necessary materials, evaluating supplier performance, and negotiating terms and conditions. Effective sourcing ensures a reliable supply of quality inputs at the best possible cost. It also involves building strong relationships with suppliers to ensure consistent delivery and performance. Proper sourcing strategies help mitigate risks and contribute to overall supply chain efficiency.
What is supply chain production?
Supply chain production centers on the manufacturing or assembly of goods. This stage encompasses production scheduling to optimize the use of resources and minimize downtime. It also involves rigorous quality control to ensure that products meet required standards and specifications. Managing the conversion of raw materials into finished products efficiently is crucial for maintaining a smooth workflow. Effective production management helps ensure timely delivery and reduces waste, contributing to overall supply chain effectiveness.
What is supply chain execution
Supply chain execution manages the distribution and delivery of finished products to customers. This stage covers order fulfillment, ensuring that orders are processed accurately and shipped promptly. It also includes transportation management, which involves selecting carriers, optimizing routes, and controlling shipping costs. Logistics management coordinates the movement and storage of goods to ensure timely and efficient delivery. Effective execution ensures customer satisfaction and helps maintain a seamless flow of products from warehouse to end user.
What is the reverse supply chain?
The reverse supply chain manages the process of returning defective or excess products. This stage involves reverse logistics, which coordinates the return of goods from customers back to the manufacturer or retailer. Returns management ensures that returned items are processed efficiently, whether for repair, refurbishment, or disposal. It also includes addressing customer complaints to resolve issues and improve service. Effective management of the reverse supply chain helps recover value from returns and maintain customer satisfaction.
What are the benefits of supply chain execution?
Using supply chain execution software to manage distribution and delivery ensures a seamless flow of products from warehouse to end user. According to Amit Levy, executive vice president of sales and strategy at Made4net, “Customers expect more, with faster and less expensive orders, all of which puts new demands on the warehouse. Warehouse operations across all industries have to be more efficient, faster and more accurate or risk losing customers to the next closest competitor.”
With a supply chain execution system in place, warehouses can improve order accuracy, reduce delivery times, and provide real-time tracking information to enhance the customer experience. At the same time, they get the information they need for proactive decision-making and quick response to issues. Effective supply chain execution also leads to substantial cost reductions by decreasing labor requirements, lowering error rates, and optimizing resource utilization.
Different types of supply chain execution systems
Supply chain execution software integrates various supply chain execution functions such as order fulfillment, inventory management, warehouse management, transportation management, supplier coordination, and logistics execution. Common supply chain execution systems include:
- Warehouse Management Systems (WMS):
- Purpose: Optimizes warehouse operations by managing inventory, order fulfillment, and storage.
- Features: Inventory tracking, order picking, packing, shipping, labor management, replenishment, parcel carrier integration, WCS automation and robotics orchestration and returns management.
- Learn more about the importance of a warehouse management system and the benefits of a WMS here.
- Transportation Management Systems (TMS):
- Purpose: Manages transportation logistics to ensure efficient and cost-effective movement of goods.
- Features: Route optimization, carrier selection, freight cost management, Last Mile, Proof of Delivery and shipment tracking.
- Order Management Systems (OMS):
- Purpose: Manages customer orders from placement to fulfillment, integrating various channels.
- Features: Order processing, inventory synchronization, and customer communication.
- Supply Chain Visibility Platforms:
- Purpose: Provides real-time visibility into the entire supply chain, from suppliers to end customers.
- Features: Tracking and monitoring of shipments, inventory levels, and order status.
- Supply Chain Analytics Tools:
- Purpose: Analyzes supply chain data to identify trends, inefficiencies, and opportunities for improvement.
- Features: Data visualization, performance metrics, and predictive analytics.
- Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) Systems:
- Purpose: Manages interactions and performance of suppliers to ensure quality and reliability.
- Features: Supplier performance tracking, contract management, and collaboration tools.
Made4net’s supply chain execution software
Made4net’s SCExpert platform is a comprehensive supply chain execution solution that offers advanced warehouse, transportation, labor, and yard management functionalities. Available as both a cloud-based warehouse management system or on-premise solution, it provides a flexible, all-in-one suite that can be deployed individually or combined based on your needs. Unlike fragmented end-to-end solutions, SCExpert features an integrated suite built on a unified technology stack, allowing seamless integration with existing backend systems. This approach simplifies adding new features, such as route optimization or proof of delivery, and adapting to evolving business requirements. Learn more by speaking with one of our supply chain execution experts today.


